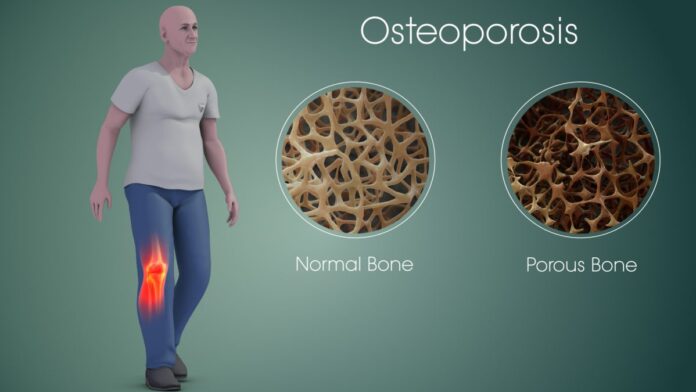
Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. This article will explore the key aspects of osteoporosis, including prevention strategies, diagnostic tools, and the various treatment options available. Understanding and managing osteoporosis is essential to maintaining bone health, especially as we age.
1. Prevention of Osteoporosis
Preventing osteoporosis starts with maintaining strong bones throughout life. Key factors include a nutrient-rich diet, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyle choices.
Nutrition: Consuming calcium-rich foods like dairy, leafy greens, and fortified products helps maintain bone strength. Vitamin D, found in fish, eggs, and sunlight exposure, enhances calcium absorption.
Exercise: Weight-bearing activities like walking, jogging, and resistance training stimulate bone growth. Flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga, can prevent falls, reducing the risk of fractures.
Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can weaken bones over time. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial, as being underweight can increase the risk of bone loss.
Pros: Reduces the likelihood of osteoporosis, promotes overall health.
Cons: Requires long-term commitment to diet, exercise, and healthy habits.
2. Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Early diagnosis is critical to managing osteoporosis effectively. A bone density test (DEXA scan) is the primary method for diagnosing osteoporosis or determining bone health risks.
Bone Density Test (DEXA): This non-invasive test measures bone mineral density (BMD), comparing it to average values for a healthy individual. It is especially recommended for women over 65, men over 70, and those with risk factors like family history, previous fractures, or chronic medical conditions.
Other Tests: Blood tests may be performed to assess calcium and vitamin D levels, while X-rays may be used to identify existing fractures.
Pros: Allows for early detection and targeted intervention.
Cons: Testing may be costly without insurance, and not all risk factors are detectable by scans.
3. Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
Treating osteoporosis focuses on strengthening bones, reducing fracture risk, and improving quality of life. Treatments include medications, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Medications: Common osteoporosis medications include bisphosphonates, which slow bone loss, and denosumab, which reduces fracture risk. Hormone-related therapies may also be used for postmenopausal women. Newer treatments like romosozumab, an antibody treatment, stimulate bone growth.
Lifestyle Adjustments: In addition to medication, individuals should continue exercising and eating a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures like vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty can help repair spinal fractures by injecting bone cement to stabilize the spine.
Pros: Medications can effectively slow bone loss, and surgical options offer relief for serious fractures.
Cons: Medications may have side effects, such as digestive issues or rare complications like jaw problems.
4. Bone Health Maintenance
Osteoporosis treatment is not just about medication—it’s about adopting a lifelong approach to bone health. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider, continued exercise, and ensuring optimal nutrition are essential parts of the long-term management plan.
Bone-Healthy Diet: Include more calcium and vitamin D, along with nutrients like magnesium and potassium. These can be found in nuts, seeds, vegetables, and whole grains.
Routine Checkups: Regular bone density testing helps track the effectiveness of treatments and monitor bone health.
Fall Prevention: Reducing the risk of falls is critical for people with osteoporosis. Modifications in the home, such as adding grab bars and removing tripping hazards, can make a significant difference.
Pros: Improves long-term bone health, reduces fracture risk, enhances overall well-being.
Cons: Requires consistent effort and lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion
Maintaining bone health and managing osteoporosis involves a combination of prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment. By focusing on nutrition, exercise, and regular health check-ups, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis or manage it effectively if diagnosed. With the right approach, it’s possible to maintain strong, healthy bones well into old age.