Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, Diet, and Treatment
Early Symptoms of Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation
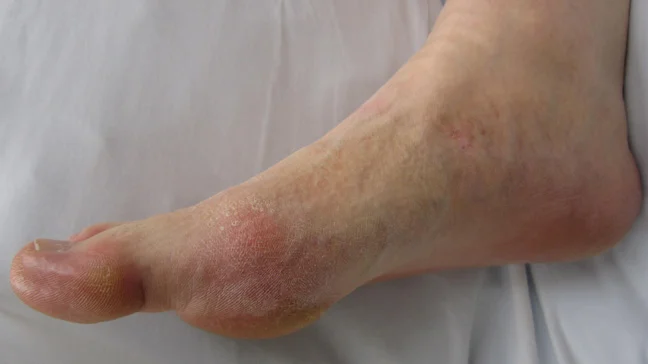
Uric acid, a waste product resulting from the breakdown of purines in food, can lead to significant health issues, most notably gout—a form of inflammatory arthritis. One of the hallmark early symptoms is sudden and intense pain, particularly in the joints, most commonly in the big toe. This pain can strike unexpectedly, often in the middle of the night, leaving individuals feeling like they’ve been hit by a freight train. Alongside the pain, you might notice redness, swelling, and tenderness around the affected joint, making even the lightest touch unbearable.
It’s not just a fleeting discomfort; these early signs are crucial indicators that something is off. Ignoring them can lead to more severe episodes, affecting your overall mobility and quality of life. Awareness of these symptoms is essential, as early intervention can make a world of difference in managing the condition and preventing it from spiraling out of control.
Chronic Symptoms of Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation
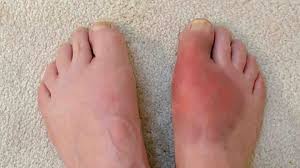
If high uric acid levels are left unchecked, they can lead to chronic joint inflammation. This condition typically manifests through recurrent gout attacks, causing persistent discomfort and swelling in the joints. Over time, these attacks may become more frequent and severe, leading to ongoing joint stiffness and a significant reduction in your range of motion. The presence of tophi—small, firm lumps of uric acid crystals under the skin—can be alarming and painful.
Chronic symptoms often leave individuals grappling with discomfort in multiple joints, making everyday activities challenging. Unfortunately, persistent high uric acid levels may also contribute to other serious health issues, including kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. Recognizing and addressing these chronic symptoms early on is vital to prevent lasting damage to the joints and overall health.
Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests for Uric Acid Levels

When it comes to diagnosing high uric acid levels and the associated inflammation, healthcare professionals have several tools at their disposal. The most common method is the serum uric acid test, which measures the concentration of uric acid in your blood. Generally, levels above 6.8 mg/dL indicate a problem. If your doctor suspects gout, they may perform a joint fluid analysis, extracting fluid from the affected joint to look for urate crystals.
Imaging tests, like X-rays or ultrasounds, can also provide insight into joint damage and inflammation. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels is essential for those with a history of gout or high uric acid. These tests not only help manage current conditions but also prevent future complications. Being proactive in your healthcare can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Precautions for Managing Uric Acid Levels

Managing uric acid levels effectively requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle changes and preventive measures. Staying well-hydrated is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to help your body flush out uric acid. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to dilute uric acid in your blood.
It’s equally important to be mindful of your diet. Limiting alcohol intake—particularly beer and spirits—can significantly reduce uric acid levels. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obesity can increase uric acid production and hinder its elimination. Additionally, cutting back on foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, can make a substantial difference. Regular exercise is also key, as it can help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall well-being.
Harmful Diets for Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation
Diet plays a crucial role in managing uric acid levels and, by extension, joint health. Certain foods are notorious for their high purine content and should be limited or avoided entirely. Red meats, organ meats, and specific seafood—like sardines and mussels—can raise uric acid production in the body, exacerbating inflammation.
Sugary beverages, especially those sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup, can also lead to spikes in uric acid levels. Processed foods high in unhealthy fats and low in essential nutrients can further aggravate inflammation in your joints. Alcohol, particularly beer and liquor, poses a significant risk, so it’s wise to limit your consumption.
Even some vegetables, such as spinach and asparagus, while healthy, contain moderate purine levels and should be consumed in moderation. Being aware of these dietary factors is essential for managing uric acid levels and reducing the risk of painful gout attacks.
Best Diets for Managing Uric Acid Levels
To effectively manage uric acid levels and alleviate joint inflammation, focusing on a balanced, low-purine diet is essential. Start by incorporating plenty of fruits and vegetables, especially those high in vitamin C, such as cherries, strawberries, and citrus fruits. These not only add flavor but may also help lower uric acid levels.
Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa provide healthy carbohydrates and should form the basis of your meals. Low-fat dairy products, including yogurt and skim milk, are also beneficial due to their protein content. Nuts and seeds can offer healthy fats without the purines found in animal proteins.
Staying hydrated is equally crucial. Drinking plenty of water helps dilute uric acid and promotes its elimination. Adopting these dietary practices, combined with regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, can significantly improve your joint health and overall well-being.
Latest Treatments for Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation in the USA

In the United States, the treatment landscape for high uric acid levels and associated joint inflammation is evolving. For immediate relief during gout attacks, healthcare providers commonly prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which help alleviate pain and inflammation. Colchicine, another effective medication, reduces inflammation and can prevent future attacks.
For long-term management, urate-lowering therapies like allopurinol and febuxostat are widely used to maintain lower uric acid levels in the bloodstream. For patients who do not respond to conventional treatments, newer biologic therapies such as pegloticase are available. These medications can significantly enhance symptoms and lower uric acid levels.
Lifestyle modifications, including dietary adjustments and regular exercise, remain crucial components of any treatment plan. As research continues, innovative therapies are emerging to enhance the management of uric acid-related conditions, providing patients with effective options for relief and prevention.
Herbal Treatments for Uric Acid and Joint Inflammation Worldwide

Herbal treatments are gaining traction around the globe as complementary approaches for managing uric acid levels and joint inflammation. Herbs like ginger and turmeric are celebrated for their anti-inflammatory properties and can be effective in reducing joint pain associated with gout. Ginger, in particular, can be consumed as a tea or incorporated into meals for added benefits.
Nettle leaf extract is another herbal remedy believed to help lower uric acid levels, often consumed in herbal teas or supplements. Dandelion root is also gaining attention for its potential to support kidney function and aid in uric acid elimination.
While herbal treatments can provide valuable benefits, it’s important to consult healthcare professionals before adding them to your regimen, especially if you’re already taking prescribed medications. Combining traditional medical treatments with herbal remedies may offer a holistic approach to effectively managing uric acid and joint inflammation, helping you regain control over your health and well-being.

